NPR’s sites use cookies, similar tracking and storage technologies, and information about the device you use to access our sites (together, “cookies”) to enhance your viewing, listening and user experience, personalize content, personalize messages from NPR’s sponsors, provide social media features, and analyze NPR’s traffic. This information is shared with social media, sponsorship, analytics, and other vendors or service providers. See details.
You may click on “Your Choices” below to learn about and use cookie management tools to limit use of cookies when you visit NPR’s sites. You can adjust your cookie choices in those tools at any time. If you click “Agree and Continue” below, you acknowledge that your cookie choices in those tools will be respected and that you otherwise agree to the use of cookies on NPR’s sites.
- Enjoy options to cover yourself, your spouse, kids and even your parents
- Enjoy access to 10,000+ hospitals for cashless treatment
- Reduce your taxable income by up to Rs. 50,000 deduction under section 80D**
With healthcare costs on the rise, purchasing a health insurance policy with a comprehensive coverage has become a must if you want to safeguard your savings and avoid going through financial hassles in the event of a medical emergency. When you purchase a health insurance policy, your insurance provider will offer you a cover against medical expenses that you might incur in case of a hospitalisation or a medical treatment.
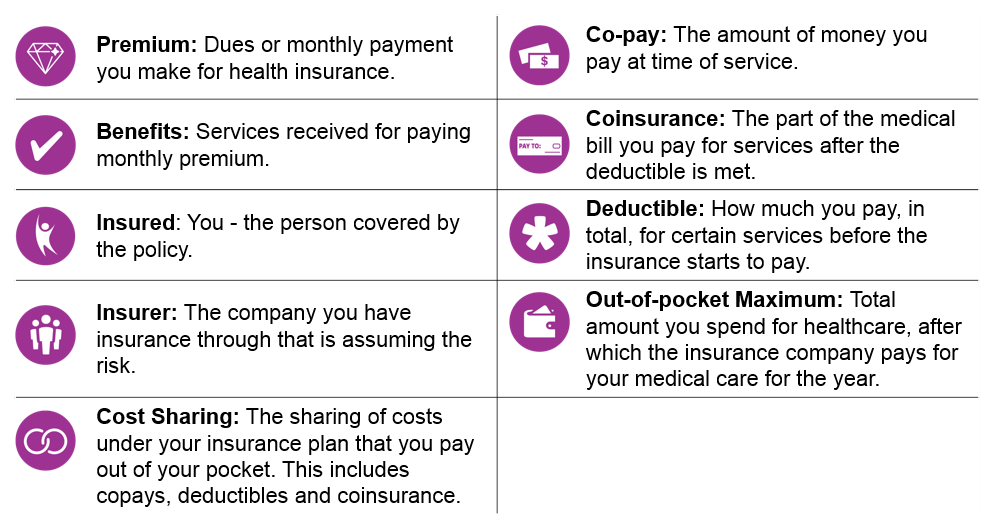
Copay in Health Insurance refers to the percentage of the claim amount that has to be borne by the policyholder under a health insurance policy. Few insurance policies come with a mandatory clause for copayment, while others offer policyholders the option for voluntary copayment, which allows them to reduce their premium payment. Insurance companies use copayments to share health care costs to prevent moral hazard. It may be a small portion of the actual cost of the medical service but is meant to deter people from seeking medical care that may not be necessary (e.g., an infection by the common cold). You pay this for each. Benefit period: Days 1-60: $1,364 deductible. Days 61-90: $341 coinsurance each day. Days 91 and beyond: $682 coinsurance per each “lifetime reserve day” after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime). Copays and deductibles are both features of most insurance plans. A deductible is an amount that must be paid for covered healthcare services before insurance begins paying. Copays are typically.
Based on the type of claim you raise (cashless or reimbursement), your insurance provider will either settle your medical bills directly with the hospital or reimburse you for the same. While a health insurance policy can be a great way to reduce the expenses that you may incur in the event of a hospitalisation, you will still have to pay a part of the hospitalisation bills if your policy came with a co-pay clause or if you opted for co-pay at the time of purchasing the plan.
What is Co-Pay?
Co-pay refers to that portion of the claim amount that is to be borne by the policyholder. While certain health insurance policies come with a mandatory co-pay clause, other health insurance plans give policyholders the option to choose a co-pay percentage as per their needs. Opting for a high co-pay will lower your premium payable, but will increase the amount that you have to pay in the event of a claim. Similarly, opting for a low co-pay will increase your premium payable, but will reduce the amount that you have to pay in the event of a claim.
Thus, for example, if you have opted for a co-pay of 10% and you raise a claim for Rs.10,000, the insurance provider will pay only 90% of the claim amount. The remaining 10% or Rs.1,000 will have to be borne by you.
Types of Co-Pay Clauses
Not all health insurance policies come with a mandatory co-pay clause. The co-pay clause may be applied to health insurance plans in the following manner:
- Co-Pay on all Medical Bills: In this case, the co-pay clause, whether mandatory or voluntary, is applied to all claims that are raised. Thus, the policyholder will need to pay a part of the claim amount for all claims raised.
- Co-Pay on Senior Citizen Policies: Most health insurance plans that are offered to senior citizens come with an inbuilt co-pay clause since treatment costs for senior citizens are usually quite expensive.
- Co-Pay for Reimbursement Claims or Treatment at Non-Network Hospitals: Certain insurance providers will specify a co-pay clause only for reimbursement claims or treatments undertaken at non-network hospitals. In this case, cashless claims will be borne fully by the insurer.
- Co-Pay for Hospitalisation in Metro Cities: Hospitalisation costs at a metro city are usually much higher than treatment costs at a smaller city or town. Thus, insurers might add a co-pay clause for treatments undertaken at large cities.
Why do Health Insurance Policies have a Co-Pay Clause
- To avoid unnecessary claims: In health insurance, there is no limit to the number of claims that a policyholder can make during a given policy year. Policyholders can continue making claims until the sum insured is completely exhausted. Thus, having a co-pay clause will reduce the chances of policyholders raising claims for small treatments/hospitalisations.
- To reduce the risk for the insurer: When there is a co-pay clause in the policy, the insured is expected to pay a certain part of the claim amount. Thus, in such a case, the insurer will not have to pay 100% of the claim amount, which, in turn, reduces the risk for the insurance company.
- To encourage judicious use of the policy: Having a co-pay component in your health insurance policy is one way for insurers to ensure that you use your policy judiciously. It also helps prevent fraudulent claims to a large extent.
- To lower premium amounts: Opting for co-pay will reduce the premium payable significantly. Thus, policyholders who don’t have too many health concerns and are looking to reduce their premium rate can opt for co-pay.
Copay Health Insurance Plans
Things to Consider before Opting for a Co-Pay
Given how affordable a policy with a co-pay clause can be, it can be tempting to purchase a health insurance plan with a high co-pay percentage. However, before you purchase such a policy, make sure to understand your coverage needs and ascertain if you have the finances to pay for your part of the hospitalisation bills in case of an unplanned or planned hospitalisation.
FAQs on co-pay under health insurance

- How do I know how much I have to pay as co-pay at the time of claim settlement?
- Why are policies with the co-pay clause cheaper?
- Is co-pay the only way I can reduce the premium payable?
- Is co-pay applicable to cashless hospitalisation?
- Can co-pay be applied for specific benefits?
Your policy document will have details regarding co-pay – whether or not you should pay and if you need to pay, then what the percentage is. Make sure you read the policy document at the time of purchase so that you do not miss out on such fine details.
The co-pay clause reduces the insurer’s risk of paying a large amount. Since the co-pay clause keeps the insured in check, in terms of raising claims frequently or making fraudulent claims, the health insurance company offers the policy at a cheaper price than one that does not have a co-pay clause.
No, there are many ways by which you can save on your premium such as only choosing a sum insured amount that you require, not opting for unnecessary benefits or add-ons, maintaining a claim-free year, purchasing the policy online, etc.
Most insurance companies apply the co-pay clause only for reimbursement claims to encourage policyholders to get treatments in network hospitals. The insurer usually covers the complete expenses incurred by the insured person at a network hospital.
Yes, the co-pay clause can be applied to specific benefits such as the room rent. Choosing an A/C room or a suite may attract co-pay while regular rooms will not. Also, the benefit payable for the treatment of a critical illness or domiciliary hospitalisation expenses may require the policyholder to share the expenses incurred.
Health Insurance Plans With Copays

All Copay Health Insurance Plans
| Health Insurance Sitemap | Health Insurance Blog | Health Insurance Reviews |
