- Restart Ssh Client Windows
- Restart Ssh Client Ubuntu
- Restart Vsphere Web Client Ssh
- Mac Restart Ssh Service
- Restart Ssh Server Ubuntu
- Restart Ssh Client Download
- To restart SSH in solaris you can use the svcs command to view the current status of the service root@solaris:# svcs grep ssh online. Computer How To How To, Tutorial, Example, Review. Restart SSH in Solaris 11. Admin Solaris 0. To restart SSH in solaris you can use the svcs command to view the current status of the service.
- TEctia® SSH client/server Secure file transfer & remote access with the gold-standard solution. Save time, guarantee business continuity and get peace of mind with the leading enterprise software for fast encrypted file transfers and secure remote access.
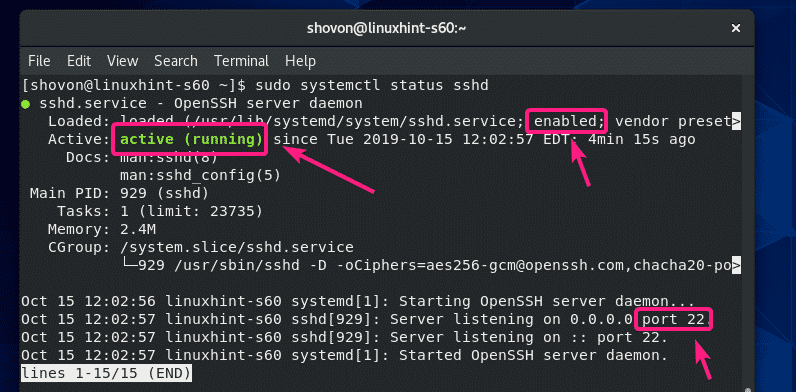
How to restart the SSHD service on Windows.
Requirements user or command shell need elevated privileges
Note: Any users connected to the SSH server will be disconnected when the SSH is restarted.
The GSW SSH Server reads configuration values each time the GSW_SSHD service is started. It is the mechanism to read the configuration registry keys into the SSH Server and apply those values.
Two options for re-starting the GSW SSH Service are:
Option 1: In the Windows Start, Search or Run command enter services.msc and press enter
- Select the Extended tab at the bottom
- Select Georgia Softworks GSW_SSHD service
Click Restart the service.
Figure 1: Restart SSHD Services for Windows
The Georgia SoftWorks GSW_SSHD service and the Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server should both have a status of Started and a Startup Type of Automatic. Using the Windows Services utility is the recommended method to start and stop the GSW services when required.
Yes, you can restart the Apache server with the help of an ssh command. If you want to go for the graphical option, you can also restart it with the help of your cPanel account. Restarting through SSH. The Apache server can be restarted with the help of the command line by using the following command. For Ubuntu based Operating System.
| Option 2: | You may use a batch program or windows command shell to restart SSH service. In the Windows Start Menu, search box type in cmd.exe and in the results right click cmd.exe and select Run as administrator. |
In the command shell enter the following.
net stop gsw_sshd && net start gsw_sshd
Figure 2: Command shell to restart the GSW SSHD Service
Confirm that the GSW SSH Service is running.
Using the Installation Status Program Item within Georgia SoftWorks UTS program group, you can view the Installation Status of the GSW UTS and SSH Server.
Figure 3: SSH Service Installation Status
View the row “Georgia SoftWorks SSH Shield”. The far right column “running” should have a ✔ check in the check box as shown above.
Watch How to restart SSH service on Windows
Back to SSH Server FAQ
Document Number: FAQ-SSH-EX030001081519
Name

autossh - monitor and restart ssh sessions
Synopsis
autossh [-V] [-Mport[:echo_port]] [-f] [SSH_OPTIONS]
Description
autossh is a program to start a copy of ssh and monitor it, restarting it as necessary should it die or stop passing traffic.
The original idea and the mechanism were from rstunnel (Reliable SSH Tunnel). With version 1.2 of autossh the method changed: autossh uses sshto construct a loop of ssh forwardings (one from local to remote, one from remote to local), and then sends test data that it expects to get back. (The idea isthanks to Terrence Martin.)
With version 1.3, a new method is added (thanks to Ron Yorston): a port may be specified for a remote echo service that will echo back the test data. Thisavoids the congestion and the aggravation of making sure all the port numbers on the remote machine do not collide. The loop-of-forwardings method remainsavailable for situations where using an echo service may not be possible.
Controlling Ssh
SSH exits
autossh tries to distinguish the manner of death of the ssh process it is monitoring and act appropriately. The rules are:
2.' If autossh itself receives a SIGTERM, SIGINT, or a SIGKILL signal, it assumes that it was deliberately signalled, and exits after killing thechild ssh process;3.' If autossh itself receives a SIGUSR1 signal, it kills the child ssh process and starts a new one;
4.' Periodically (by default every 10 minutes), autossh attempts to pass traffic on the monitor forwarded port. If this fails, autossh willkill the child ssh process (if it is still running) and start a new one;
5.' If the child ssh process dies for any other reason, autossh will attempt to start a new one.
Startup behaviour
If the ssh session fails with an exit status of 1 on the very first try, autossh
1.' will assume that there is some problem with syntax or the connection setup, and will exit rather than retrying;
2.' There is a 'starting gate' time. If the first ssh process fails within the first few seconds of being started, autossh assumes that it never madeit 'out of the starting gate', and exits. This is to handle initial failed authentication, connection, etc. This time is 30 seconds by default, and can beadjusted (see the AUTOSSH_GATETIME environment variable below). If AUTOSSH_GATETIME is set to 0, then both behaviours are disabled: there is no 'startinggate', and autossh will restart even if ssh fails on the first run with an exit status of 1. The 'starting gate' time is also set to 0 when the -f flagto autossh is used.
Continued failures
If the ssh connection fails and attempts to restart it fail in quick succession, autossh will start delaying its attempts to restart, graduallybacking farther and farther off up to a maximum interval of the autossh poll time (usually 10 minutes). autossh can be 'prodded' to retry bysignalling it, perhaps with SIGHUP ('kill -HUP').
Connection setup
As connections must be established unattended, the use of autossh requires that some form of automatic authentication be set up. The use ofRSAAuthentication with ssh-agent is the recommended method. The example wrapper script attempts to check if there is an agent running for the currentenvironment, and to start one if there isn't.
It cannot be stressed enough that you must make sure ssh works on its own, that you can set up the session you want before you try to run it underautossh
If you are tunnelling and using an older version of ssh that does not support the -N flag, you should upgrade (your version has security flaws). Ifyou can't upgrade, you may wish to do as rstunnel does, and give ssh a command to run, such as 'sleep 99999999999'.
Options
specifies the base monitoring port to use. Without the echo port, this port and the port immediately above it ( port + 1) should be something nothingelse is using. autossh will send test data on the base monitoring port, and receive it back on the port above. For example, if you specify '-M 20000',autossh will set up forwards so that it can send data on port 20000 and receive it back on 20001.Alternatively, a port for a remote echo service may be specified. This should be port 7 if you wish to use the standard inetd echo service. When an echoport is specified, only the specified monitor port is used, and it carries the monitor message in both directions.
Many people disable the echo service, or even disable inetd, so check that this service is available on the remote machine. Some operating systems allow oneto specify that the service only listen on the localhost (loopback interface), which would suffice for this use.
The echo service may also be something more complicated: perhaps a daemon that monitors a group of ssh tunnels.
Setting the monitor port to 0 turns the monitoring function off, and autossh will only restart ssh upon ssh's exit. For example, if you are using a recentversion of OpenSSH, you may wish to explore using the ServerAliveInterval and ServerAliveCountMax options to have the SSH client exit if it findsitself no longer connected to the server. In many ways this may be a better solution than the monitoring port.
-f' causes autossh to drop to the background before running ssh. The -f flag is stripped from arguments passed to ssh. Note that there is acrucial a difference between -f with autossh, and -f with ssh: when used with autossh ssh will be unable to ask for passwords orpassphrases. When -f is used, the 'starting gate' time (see AUTOSSH_GATETIME) is set to 0.
Restart Ssh Client Windows
-V' causes autossh to display its version number and exit.
Environment
Other than the flag to set the connection monitoring port, autossh uses environment variables to control features. ssh seems to be still collectingletters for options, and this seems the easiest way to avoid collisions.
If this variable is set, the logging level is set to to LOG_DEBUG, and if the operating system supports it, syslog is set to duplicate log entries tostderr.Restart Ssh Client Ubuntu
AUTOSSH_FIRST_POLL
Specifies the time to wait before the first connection test. Thereafter the general poll time is used (see AUTOSSH_POLL below).
AUTOSSH_GATETIME
Specifies how long ssh must be up before we consider it a successful connection. The default is 30 seconds. Note that if AUTOSSH_GATETIME is set to 0, then notonly is the gatetime behaviour turned off, but autossh also ignores the first run failure of ssh. This may be useful when running autossh at boot.
AUTOSSH_LOGLEVEL
Specifies the log level, corresponding to the levels used by syslog; so 0-7 with 7 being the chattiest.
AUTOSSH_LOGFILE
Specifies that autossh should use the named log file, rather than syslog.
AUTOSSH_MAXLIFETIME
Sets the maximum number of seconds that the program should run. Once the number of seconds has been passed, the ssh child will be killed and the program willexit.
AUTOSSH_MAXSTART
Specifies how many times ssh should be started. A negative number means no limit on the number of times ssh is started. The default value is -1.
AUTOSSH_MESSAGE
Append message to echo message sent when testing connections.
AUTOSSH_NTSERVICE
(Cygwin only.) When set to 'yes' , autossh sets up to run as an NT service under cygrunsrv. This adds the -N flag for ssh if not already set, sets the logoutput to stdout, and changes the behaviour on ssh exit so that it will restart even on a normal exit.
Restart Vsphere Web Client Ssh
AUTOSSH_PATH
Specifies the path to the ssh executable, in case it is different than the path compiled in.
AUTOSSH_PIDFILE
Write autossh pid to specified file.
AUTOSSH_POLL
Specifies the connection poll time in seconds; default is 600 seconds. If the poll time is less than twice the network timeouts (default 15 seconds) thenetwork timeouts will be adjusted downward to 1/2 the poll time.
AUTOSSH_PORT
Sets the connection monitoring port. Mostly in case ssh appropriates -M at some time. But because of this possible use, AUTOSSH_PORT overrides the -M flag. Avalue of 0 turns the monitoring function off.
Mac Restart Ssh Service
Author
autossh was written by Carson Harding.
Restart Ssh Server Ubuntu
See Also
ssh(1), ssh-add(1), ssh-agent(1), ssh-keygen(1), cygrunsrv(1).
Restart Ssh Client Download
BSD Jul 20, 2004 BSD
